This is an old revision of the document!
Menu: Collocation
One of the principal properties of interface KonText is the possibility to use statistical methods to identify collocations of a wanted word. By collocation, we understand a meaningful, fixed, syntagmatic sequence of two (or more) words in the immediate context. A collocation consists of a key word (node which usually is also KWIC) and a contextual word (collocate). The list of collocation candidates with which a wanted word or a phrase collocates forms the basis for corpus analysis as it enables us to determine what kind of context is typical for a wanted phenomenon.
Association measures are used to identify a collocation. Interface KonText presently employs the following basic ones: t-score, MI, MI3, log likelihood, min. sensitivity, logDice, MI.log_f, relative frequency. Each of the measures is sensitive to different kinds of phrases and each might not work in some cases. It is therefore recommended to combine the measures and compare their output. The statistical analysis by association measures generates a list of collocation candidates and it is up to the researcher to decide whether they really are legitimate collocations.
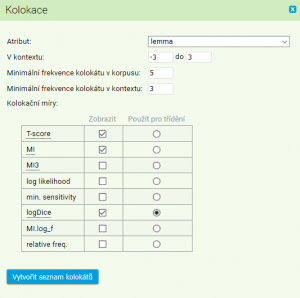
Suppose that we created a concordance of lemma dřevo in the corpus SYN2010. By clicking on the Collocation item in menu, a form for collocation analysis will appear. In the form, it is possible to specify the following values when searching the collocations within the scope of created concordance:
- Attribute: the selection of positional attribute of a collocate (we can search for surrounding lemmas of the lemma dřevo, the words or any other available attributes)
- In the range from - to: specification of the contextual span (in the proximity of KWIC) where the collocates will be searched for (negative numbers indicate the positions preceding KWIC, while the positive ones follow KWIC, cf. frequency distribution))
- Minimum frequency in corpus: -establishes minimum overall frequency of a unit to be included in the collocate list (provided that the minimum frequency is set on 5, the collocate of lemma dřevo cannot be those items that occur in the whole corpus less than 5 times)
- Minimum frequency in given range: provided that we specified the context span for collocate search from -3 to 3, then the minimum frequency in given range optiom determines how frequently should an item co-occur with KWIC to be included in the collocate list (when calculating the association measures only those items will be taken into consideration which occur at least 3 times in the proximity of KWIC, lemma dřevo in our examle)
- Show functions: which association measures will be calculated and listed for each of the collocates that the conditions specified above are met
- Sort by: according to which of the association measures will the list be sorted (especially useful for the long lists)
Collocation list
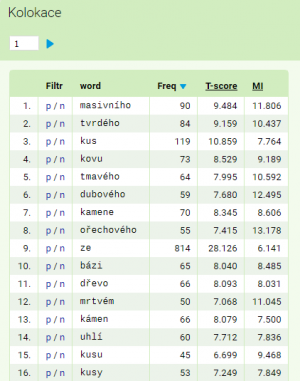
Based on the submitted specifications, lemma dřevo co-occurs with 2386 different words (attribute word) which can function as its collocates. Sorting by logDice produces a list with the following forms as the most significant collocate candidates: tvrdého, bázi, kus, kusy, dubového…
V seznamu najdeme pro každou jednotku jednak celkovou frekvenci souvýskytu vyhledaného jevu a jeho kolokátu (např. lemmatu dřevo a kolokátu tvrdého) a jednak hodnoty vybraných asociačních měr pro takovéto spojení. Při kliknutí na záhlaví tabulky je možné seznam přetřídit podle zvolené veličiny. Stejně jako ve výpisu frekvenční distribuce je i v seznamu kolokátů možné pomocí odkazů p/n vytvořit pozitivní nebo negativní filtr, který hledá kolokát v okolí původního KWICu.
Na místě je dvojí upozornění:
- V seznamu kolokátů se zobrazují všechna slova, která odpovídají specifikacím kontextového okna a minimální frekvence v korpusu a v rozsahu, bez ohledu na to, zda se skutečně o kolokát jedná či ne. Asociační míry slouží pouze k setřídění všech jednotek splňujících zadaná kritéria – to, jestli dané slovo skutečně funguje v kolokaci s vyhledaným jevem (jestli s ním např. tvoří syntagma), je otázka dalšího zkoumání, která nemůže být rozhodnuta čistě na základě hodnoty asociační míry (ta funguje spíše jako pomůcka pro odfiltrování nezajímavých a statisticky nevýznamných kolokátů na konec seznamu)
- Každá asociační míra je citlivá na jiný druh kolokací; je proto vhodné kolokační seznam procházet opakovaně po setřídění dle různých asociačních měr