This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Menu: Frequency
In interface KonText menu the item Frequency encompasses function for creating frequency distribution. With this function it is possible to get an overview of the types (e.g. of different words) in the search results, along with their frequency. If we wish to find all of the nouns in the genitive case, in the plural form, with this funtion we can determine which words occur in this particular case and number and how frequently. It is also possible to use frequency distribution to determine frequency of both the previous and the following units, calculate lemmas in the concordance or determine distribution of the wanted phenomenon across different text types and their groups (according to the genre, txtype etc.).
Frequency distribution encompasses both custom (general) settings and quick selection (both are available at the second level of menu):
- Doc IDs - assesses the whole concordance and lists the text names (structural attributes
name) in which the wanted phenomenon occurs, along with the frequency of this phenomenon in the individual texts - Text types - assesses the whole concordance and lists an overview of the structural attributes 2) which apply to the text type (structural attributes
txtype_group,txtype,med,srclang), along with their frequency (the meaning of individual abbreviations is available at the list of abbreviations and codes)
The function New query → Word list which generally applies to the entire corpus (not only to the specific concordance) allows for similar functionality.
Custom settings of frequency distribution
The form which appears after clicking on the option Frequency distribution → Custom consists of two sections:
- form for multilevel frequency distribution (which can be used to analyze positional attributes) such as word, lemma, tag etc.)
- form for frequency distribution according to the structure attributes (such as
txtype,medorsrclang)
Frequency distribution according to the positional attributes
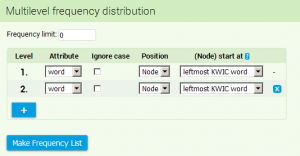
Multilevel frequency distribution enables us to calculate frequency distribution of any concordance position within the span of 6 positions to the left and 6 to the right from KWIC. At first it is necessary to select in the form which attribute we wish to calculate in frequency distribution (e.g. in SYN corpora there are available basic positional attributes ) word, lemma, tag, lc, pos, along with specific attributes k, g, c).
Afterwards, it is necessary to select whether frequency distribution should be calculated regerdless of the letter case. Selection of the option case-insensitive causes that all of the items are interpreted as having lower case, regardless of what type of case they actually have in the corpus.
In case of custom settings of frequency distribution, we do not need to restrict ourselves to KWIC only (unlike when working with quick selection). It can be calculated from any context position to the right or left from the wanted word. The item position in the form enables us to select not only positions from the lext (the preceding) context (6L-1L), but also KWIC itself and positions to the right (the following) context (1R-6R). The numbering of the positions (according to both current and older notation) is summed up in the following table:
| concordance | místnosti | . | Byly | z | těžkého | tmavého | dřeva | a | zlověstně | zaskřípaly | . | Poslepu | jsem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| position | 6L | 5L | 4L | 3L | 2L | 1L | KWIC | 1R | 2R | 3R | 4R | 5R | 6R |
| position (older notation) | -6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | KWIC | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
When determining the position of what should be the subject of calculation of frequency distribution, a problem might arise in case when the wanted KWIC is multi-word (e.g. when searching for a phrase dřevo a uhlí). In that case it is necessary to specify which position of KWIC will be the starting one for calculation (whether the right or left one). The item (Node) start at is used to perform this action. The following table sums up how the marking of contextual positions alters according to which end of the multi-word KWIC is selected as a starting point.
| concordance | znečišťování | ovzduší | . | Moderní | kotle | na | dřevo | a | uhlí | splňují | dnes | všechny | požadavky | z | hlediska |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| position (calculated from the left) | 6L | 5L | 4L | 3L | 2L | 1L | KWIC | 1R | 2R | 3R | 4R | 5R | 6R | 7R | 8R |
| position (calculated from the right) | 8L | 7L | 6L | 5L | 4L | 3L | 2L | 1L | KWIC | 1R | 2R | 3R | 4R | 5R | 6R |
If we wish to create frequency distribution of not only individual units but also pairs of words (bigrams) or even longer phrases, we have to add another level of frequency distribution. Another line will be added to the form with the identical setting options.The quick option of frequency distribution Node forms represents an easier option. - if we apply it to multi-word KWIC (e.g. when searching for two consecutive adverbs such as pomalu a opatrně [tag="D.*"][word="a"][tag="D.*"]), the wanted multi-word expressions ordered according to frequency will appear without any complicated settings.
Provided that we are satisfied with the specification, we may begin the calculation by clicking on the Make frequency list button. All of the items with at least one occurence will appear in the basic settings. If we wish to narrow the list down, we may set Frequency limit to the value which satisfies the situation.
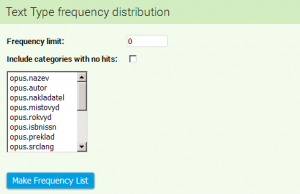
Text Type frequency distribution
The settings of Text Type frequency distribution is located in the second part of the form. It is used only in those cases when the subject of the research depends on what text types do the occurences in the concordance occur (if we are interested in txtype), srclang, medium etc.).
In the displayed list we may use the mouse to highlight the metainformation whose values we wish to calculate in the frequency distribution. If we select more than one value (by clicking on the Ctrl button), the search will result in more than one list - unlike in the previous case, this is not a multilevel analysis (in which the data from various levels combine), but successive launch of a number of different kinds of frequency distribution which results in a number of frequency lists.
Even in this form we may set the frequency limit, if we wish to restrict the number of results in the list. With the option Include categories with no hits it is also possible to display those attributes in the list which did not appear in the concordance. Lemma dřevo has not once appeared in the songs (txtype SON). Provided that this option is ticked, txtype SON will appear in the frequency distribution even with a zero frequency.
Frequency list (summary)
The following examples show how to use frequency list when working with the SYN2010 corpus to search for a query of lemma dřevo.
([lemma="dřevo"]).
- Frequency list of the words of lemma dřevo regardless of case and with a zero frequency limit.
- Frequency distribution of the values of structural attributes
txtypeandtxtype_groupof lemma dřevo (including the values with zero frequency)
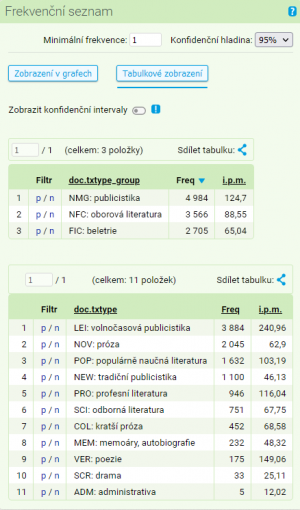
Different kinds of information will appear by every word (attribute) displayed in the frequency list of lemma dřevo. The basic informaton is located in the frequency column and displays absolute frequency of a given item in the searched concordance (if the concordance was altered in some way before the frequency list was submitted - e.g. with filters - the frequency list will be altered accordingly). In the list to the left from the word, there are located links p/n which can be used for a quick display of positive or negative filter. By clicking on the p in the line displaying frequency for the word dřevem, we filter out this form from the current concordance,in the same way when n is activated, all of the occurence of the given form will be eliminated from the current concordance.
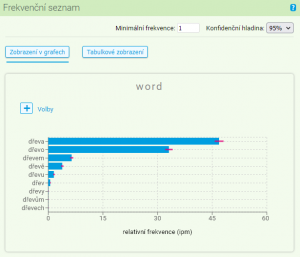
The last column of the frequency list contains a horizontal bar chart. It is used for completing the differences between absolute frequencies of the individual items (the length of the horizontal lines should correspond to the word frequency).
After clicking on the heading of the column, the table will automatically be rearranged according to the selected column. This way it is possible to create a list that is arranged alphabetically (in addition to the usual list arranged according to the frequency).
The summary of frequency list arranged according to the structural attributes has slightly different structure. Both the column with absolute frequency and column enabling quick filtering remain the same (in some cases only the option of negative filter is disabled).
In the latest version, every item (the value of the selected structural attribute) also contains i.p.m. value. It conveys the relative frequency of phenomena displayed in the concordance in relation to the overall size of the corpus part with a given value of structural attribute. In our example, lemma dřevo appears in the corpus SYN2010 with a frequency of 3509 in specialized literature. Considering the overall ratio of specialized literature in the corpus (27%), it accounts for 107,9 of instances per million of words (i.p.m.). Even though the absolute frequency of lemma dřevo is comparable in fiction and specialized literature (3276 versus 3509), considering the difference in sizes of these two sections the relative frequency in specialized literature is almost twice as big (65,9 versus 107,9).
The difference between absolute and relative frequency is also shown in the horizontal bar charts. The lenght of the line represents relative frequency, while the width represents absolute frequency. They are useful for quick examination of the results.
Just like the items, the structural attributes can also be rearranged in the table according to any column. This is especially useful when we need to know the order according to the relative frequency which allows for comparison of the number of occurences even in the corpora of different sizes.
Menu: Query • Corpora • Save • Concordance • Filter • Frequency • Collocation • View • Help